
Any web application needs to perform CRUD operations on data and refresh its state after that. Ag-Grid allows your users to easily manipulate data and immediately display any changes in it coming in from API or a server-side update.
In this blogpost, you'll get live samples showing you how to refresh ag-Grid after a data change when all data is stored on the client using the client-side row model. If you have fewer than 20,000 rows, we recommend using the client-side row model due to many built-in features it offers. ag-Grid also supports binding to server-side data for larger data sources - see the ag-Grid data source comparison here.
This sample using client-side data is implemented in all the popular web frameworks - React, Angular, VueJS. Please see the sample in action below:
Live Demos
See the live examples with code here:
We will cover two ways to implement this, one being a general approach which can be applied regardless of the "flavour" of the grid being used. The other involves changing a bound row data property, which may sound fancy but is super easy, as we'll soon see...
Contents
- Immutable Data
- Binding Row Data in React
- Binding Row Data in Angular
- Binding Row Data in Vue
- Binding Row Data in Plain JavaScript
- What's Next
Immutable Data
When you need to frequently update row data in ag-Grid, using the immutable data grid option is especially valuable. When immutable data is set, the grid can automatically work out which rows need to be updated, replaced, deleted or added when new row data is provided, rather than just replacing all of the row data and redrawing the grid completely.
This is particularly handy when the default state of the grid changes often, for example as a result of grouping or filtering. If we were to update row data without using the immutable data grid option, the grid would add the data but revert to its default state, with no filtering applied or expanded group nodes.
For this approach to work, we need to set unique IDs for all of our rows. This is done using the getRowNodeId grid callback, which is called for each row and lets us return a unique ID value for that row.
This is all that's needed to use immutable data to simplify the row data update. For additional details on how to use immutable data, please see our documentation.
Binding Row Data in React
In this section we'll be walking through an example showing how to bind the grid row data when using React.
We update the row data in the grid using the immutable data grid option and by making changes to our rowData state variable in our methods.
The code snippet below shows how to add a new row and update the grid to display it. Please see the relevant code in the addRowData method, the rowData state variable and the getRowNodeId callback below:
this.state = {
rowData: [],
...rest of the state
};
}
getRowNodeId = data => {
return data.id;
};
addRowData = () => {
let newRowData = this.state.rowData.slice();
let newId =
this.state.rowData.length === 0
? 0
: this.state.rowData[this.state.rowData.length - 1].id + 1;
let newRow = { athlete: 'new athlete', id: newId };
newRowData.push(newRow);
this.setState({ rowData: newRowData });
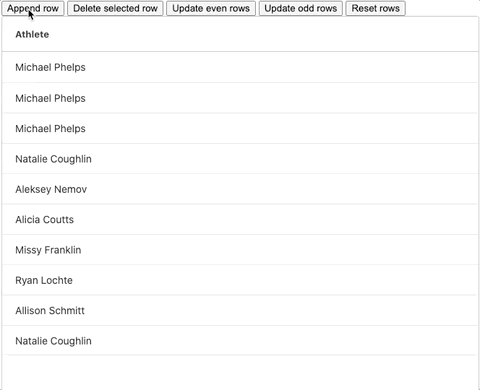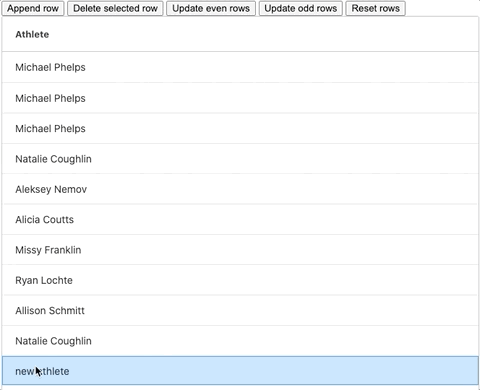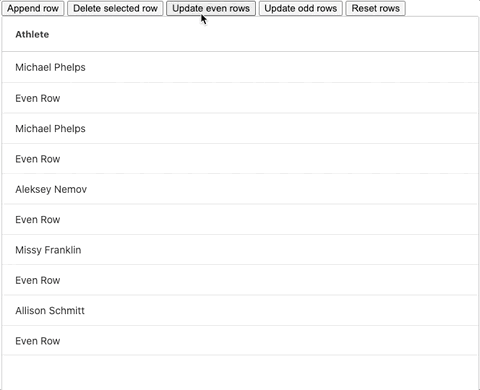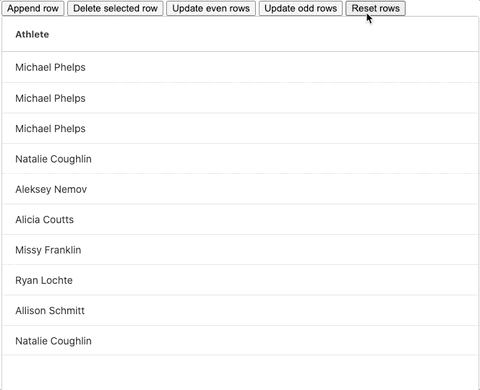
};The addRowData method is the key here. We first create a copy of our existing rowData variable, then build our new row. We then add the new row to our rowData copy and finally, we set the rowData state variable to reference the updated row data object.
Please see a GIF showing adding a new row below:
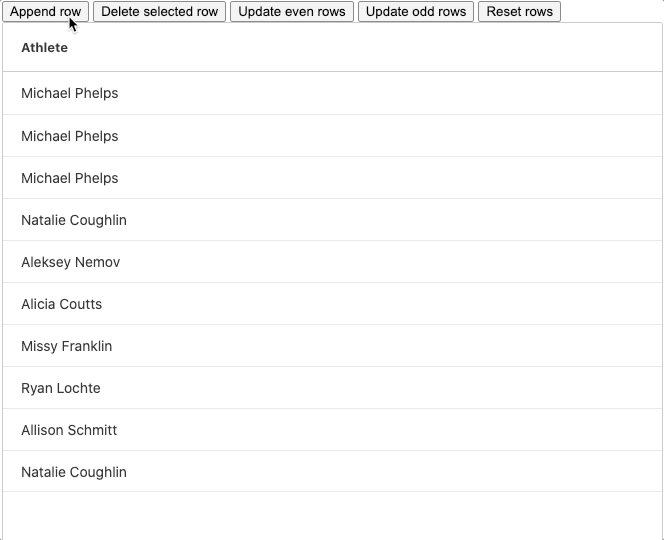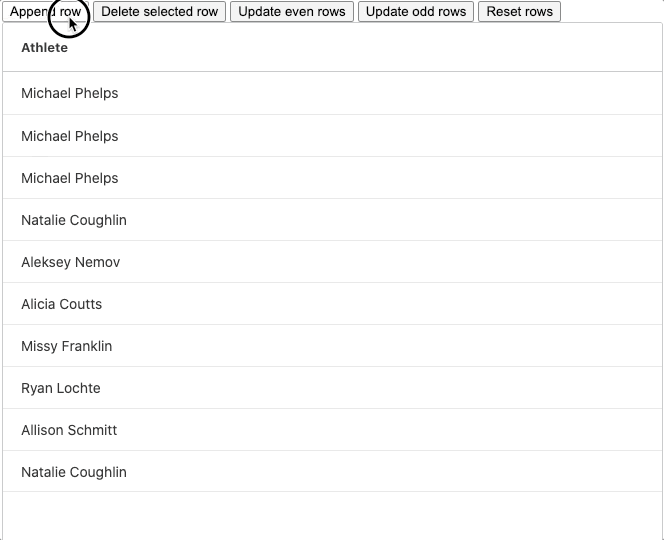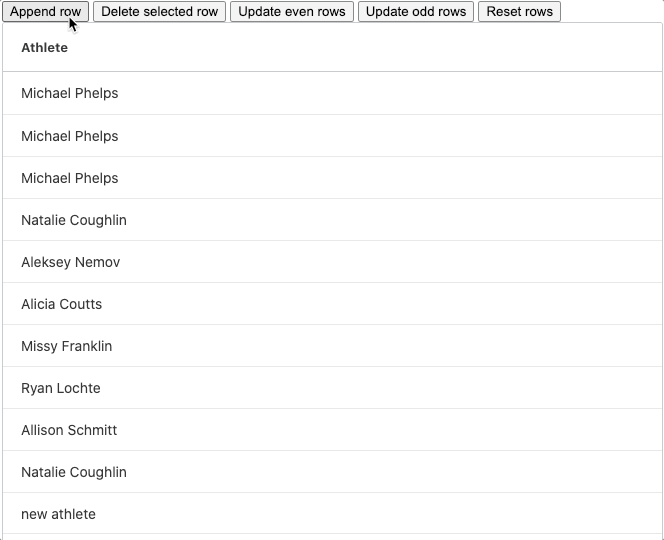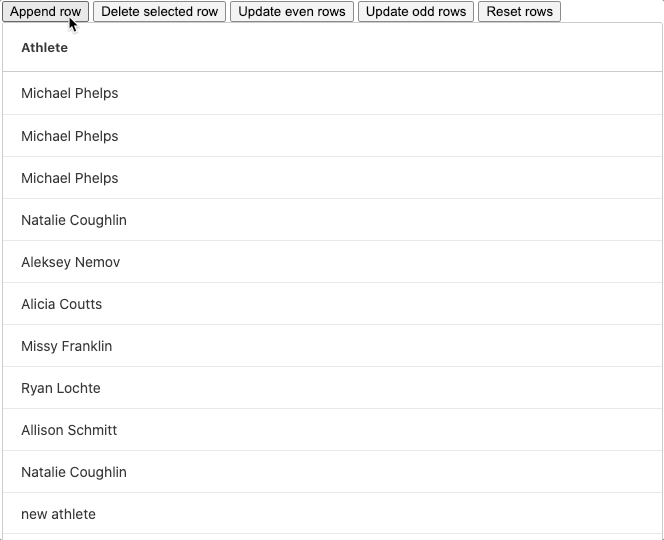
We can abstract this pattern and use it to apply the delete and update methods too. The pattern is as follows: get a copy of the current row data, make the changes to the copy and bind the copy to the grid.
The full React example can be found embedded below - please feel free to explore and play with it:
Binding Row Data in Angular
This section looks at binding the grid's row data when using Angular.
To do this, we use the immutable data grid option and make changes to the state variable the grid references for the row data. The following code snippet shows our removeRowData method, our row data variable and our getRowNodeId callback (needed for the immutable data grid option, as explained above):
private rowData: [];
constructor(private http: HttpClient) {
this.getRowNodeId = (params) =>{
return params.id
}
}
removeRowData = () =>{
let focusedNode = this.gridApi.getSelectedRows()[0]
let newRowData = this.rowData.filter(row=>{
return row !== focusedNode;
})
this.rowData = newRowData
}The removeRowData is where we make the change to the row data. First we use the getSelectedRows() API method - this returns all of the selected rows in the grid.
Our example only allows one row to be selected at a time, so the focused row will be the first (and only row) in the returned array, so we save a reference to that row (node). We then create a new array based on our current row data, we filter our current row data to remove the focused row. Finally, we update our bound row data variable to reference the new row data.
The GIF below shows this method in action:
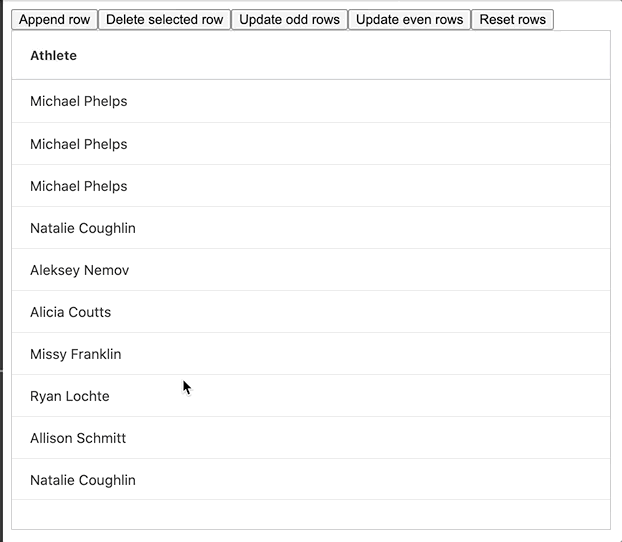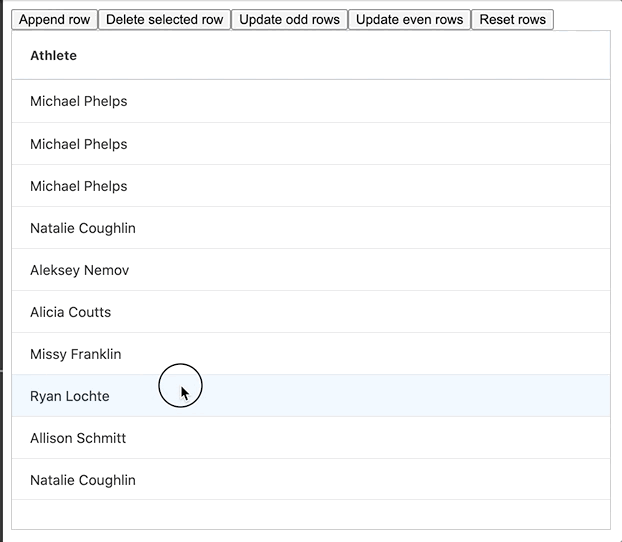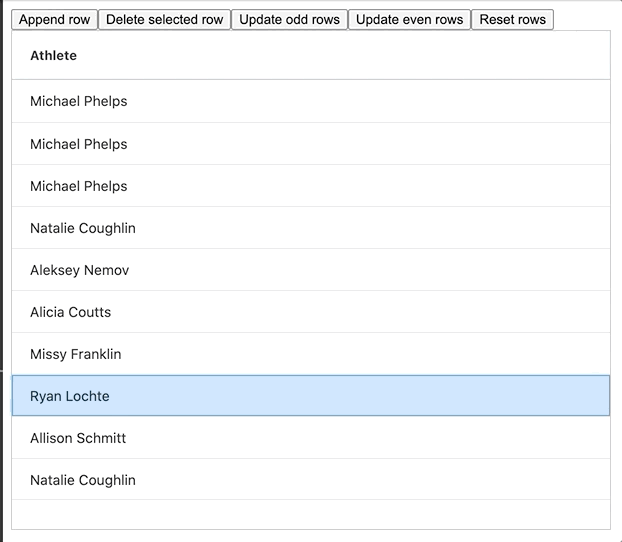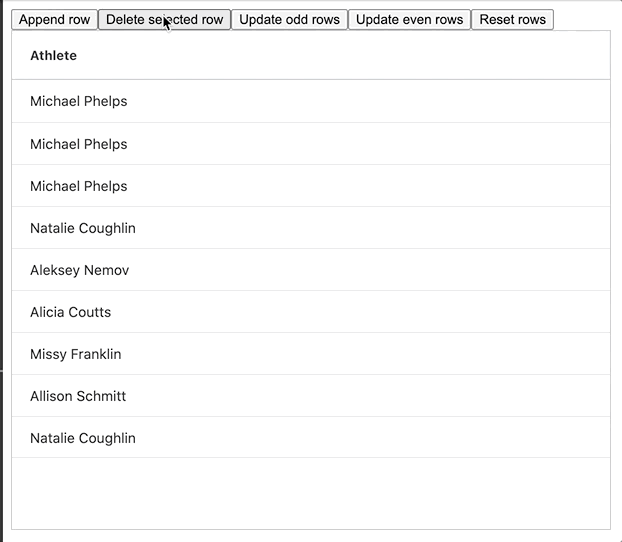
The full example can be found embedded below, please feel free to have a look and play around with it:
Binding Row Data in Vue
This section looks at binding row data while using Vue.
See below the resetRowData method from our Vue live example:
resetRowData() {
this.rowData = this.backupRowData;
},
onGridReady() {
const httpRequest = new XMLHttpRequest();
onGridReady continues...
this.rowData = data;
this.backupRowData = data;
};
onGridReady continues...
}The resetRowData method is quite simple, we update our bound row data variable to reference the row data we initially load into the grid. To achieve this, we use the onGridReady event to set our initial row data and a backup row data variable at the same time. This is the backup row data we use in our resetRowData method.
That's all there is to it! There wasn't too much to go over with this method but the live example is embedded below. Feel free to explore the rest of the methods and play around with this:
Binding Row Data in JavaScript
This section will look at how we can bind row data to the grid while using plain JavaScript. Here, we update the row data in a grid using the immutable data grid option along with the api.setRowData() method:
var gridOptions = {
getRowNodeId: data => {
return data.id;
},
immutableData: true,
...
};
const updateEvenRowData = () => {
let newRowData = rowData.map((row) => {
if (row.id % 2 === 0) {
return { ...row, athlete: "Even Row" };
}
return row;
});
rowData = newRowData;
gridOptions.api.setRowData(rowData);
};
Our updateEvenRowData method is where the row changing happens. We first make a copy of our row data array and update each even row in the process using the map function. We then update our original row data variable to reference the updated version. Once we've done this, all that's left to do is call the setRowData method with our updated row data object and see the update. In our example we bound this function to a button labelled Update Even Rows, the GIF below shows it in action:
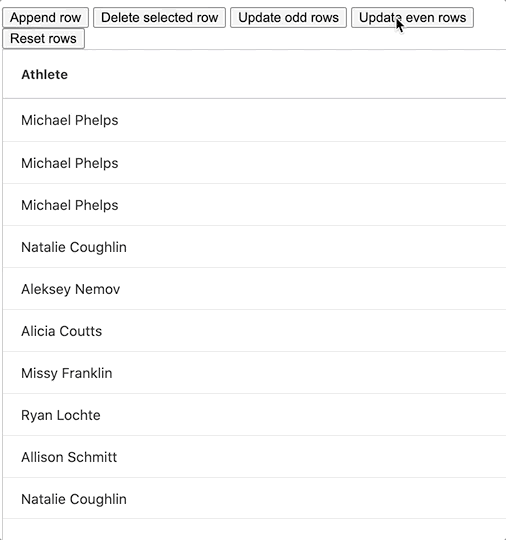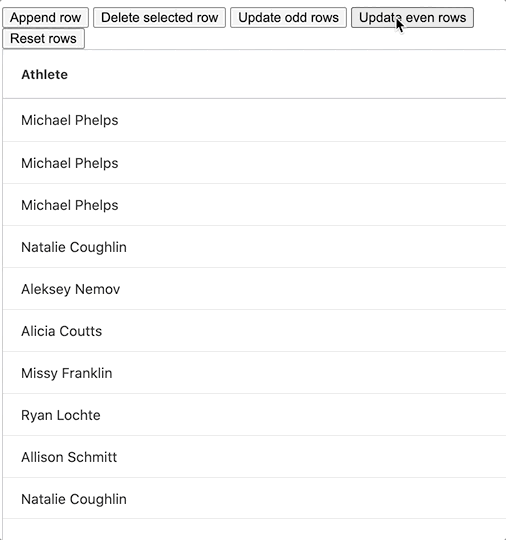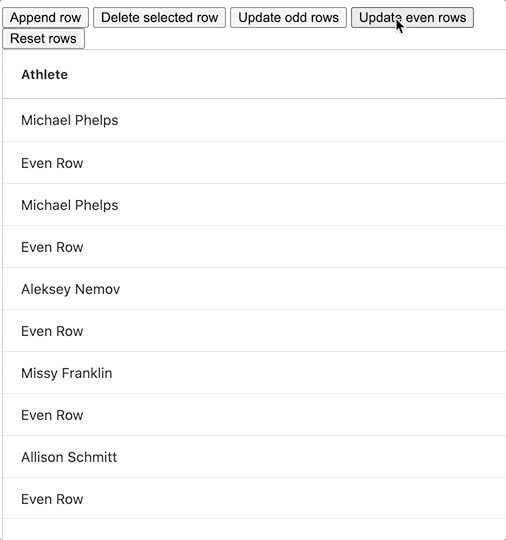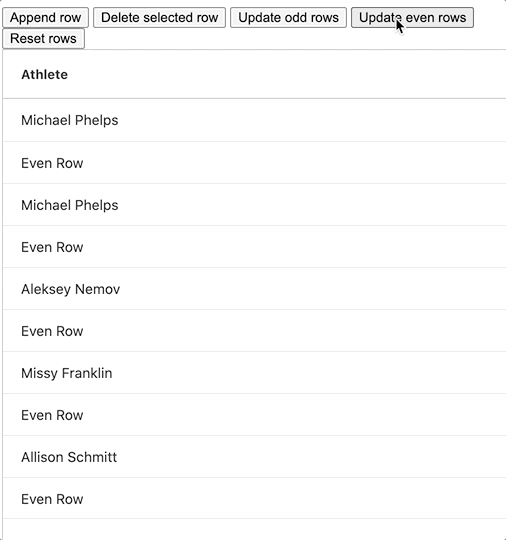
We've also added a Reset button to reset the row data to its original state with the help of our "rowDataBackup" variable.
Please feel free to play around with the example below:
What's next?
We hope this article helps you easily update the data in ag-Grid after a CRUD update. Please check out our other blog posts and documentation for a great variety of scenarios you can implement with ag-Grid.
If you would like to try out ag-Grid check out our getting started guides (JS / React / Angular / Vue)
Happy coding!
