AG Grid is now available in Reflex, allowing you to easily integrate our advanced data handling and visualization features - such as filtering, grouping, and pivoting - into your Python projects.
What is Reflex?
Reflex is an open-source framework for quickly building beautiful, interactive web applications in pure Python. Under the hood, Reflex apps compile down to a React frontend app and a FastAPI backend app. Only the UI is compiled to Javascript; all the app logic and state management stays in Python and is run on the server.
Why Reflex AG Grid?
Reflex has become more popular among Python developers in banking and fintech which makes AG Grid an obvious choice for advanced data handling, given our almost ubiquitous position within the financial and banking industry
Reflex AG Grid vs. Reflex DataTable Components
While Reflex offers a basic rx.data_table component out of the box, Reflex AG Grid takes data handling to the next level. If you're working with large datasets, need advanced filtering and sorting capabilities, or require features like editable cells and export options, Reflex AG Grid is the ideal choice.
Some key advantages of Reflex AG Grid include:
- Superior performance with large datasets
- Extensive customization options
- Built-in features like column pinning and row grouping
- Seamless integration with Reflex's reactive programming model
- Support for both free (community) and enterprise AG Grid features
Similarly to AG Grid, the core functionality of Reflex is free and open-source.
For those with more demanding or advanced requirements, our Enterprise version offers additional features such as pivot tables, advanced groupings, and Excel export capabilities.
Reflex AG Grid supports both the community and enterprise versions of AG Grid – you just need a valid AG Grid license key to unlock the enterprise features.
Getting Started with Reflex AG Grid
Follow along for a brief step-by-step guide on how to use Reflex AG Grid to build an app like the one shown below! Press the "Fetch Latest Data" button to see the app in action.
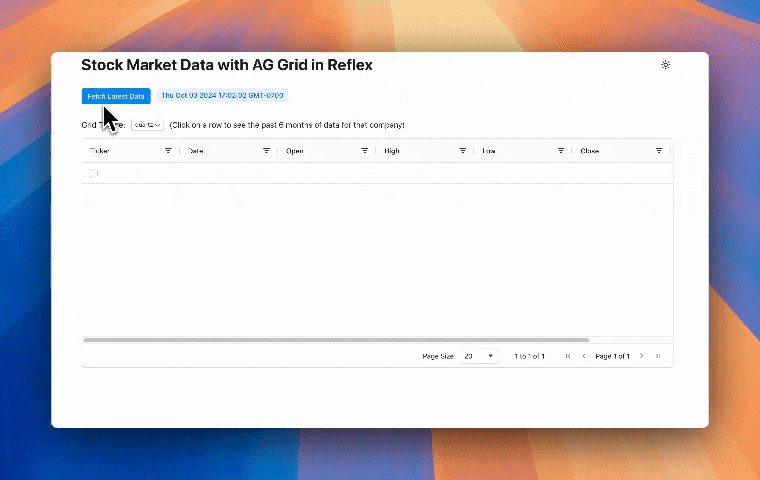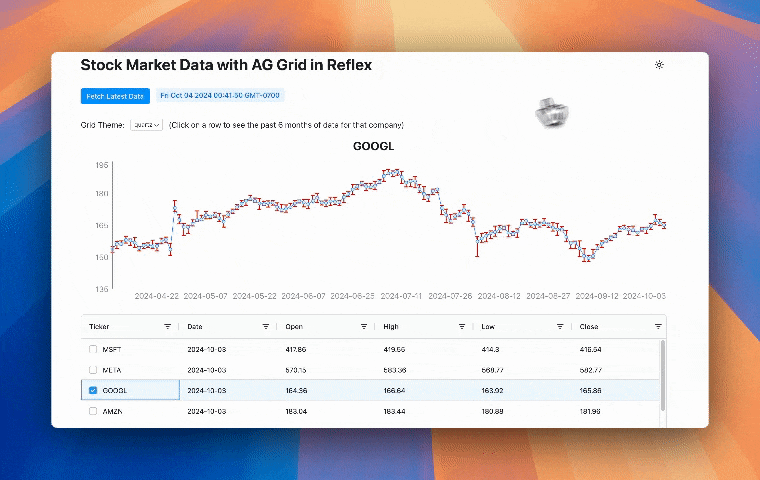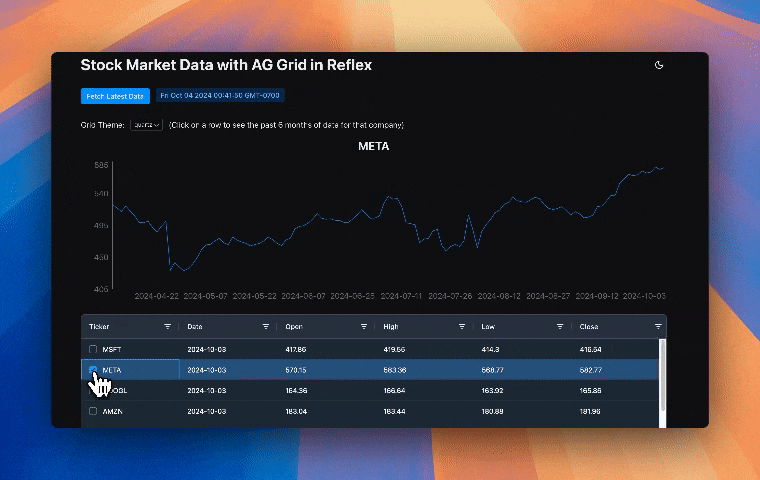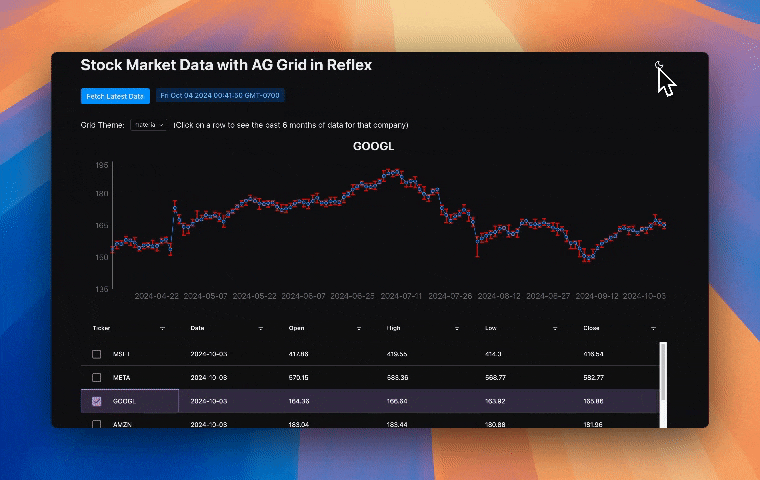
This finance app uses Reflex AG Grid to display stock data in an interactive grid with advanced features like sorting, filtering, and pagination. Selecting a row from the grid shows that companies stock data for the past 6 months in a line chart. Let's review the code to see how Reflex AG Grid is used in this app.
Setup
First, install Reflex AG Grid with pip:
pip install reflex-ag-grid
Then import the necessary libraries, including yfinance for fetching the stock data:
import reflex as rx
from reflex_ag_grid import ag_grid
import yfinance as yf
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
import pandas as pd
Fetching and transforming data
Next, we define the State class, which contains the application's state and logic:
# The list of companies to fetch data for
companies = ["AAPL", "MSFT", "GOOGL", "AMZN", "META"]
class State(rx.State):
# The data fetched from Yahoo Finance
data: pd.DataFrame
# The data to be displayed in the AG Grid
dict_data: list[dict] = [\{}]
# The datetime of the current fetched data
datetime_now: datetime = datetime.now()
def fetch_stock_data(self):
self.datetime_now = datetime.now()
start_date = self.datetime_now - timedelta(days=180)
# Fetch data for all tickers in a single download
self.data = yf.download(companies, start=start_date, end=self.datetime_now, group_by='ticker')
rows = []
for ticker in companies:
# Check if the DataFrame has a multi-level column index (for multiple tickers)
if isinstance(self.data.columns, pd.MultiIndex):
ticker_data = self.data[ticker] # Select the data for the current ticker
else:
ticker_data = self.data # If only one ticker, no multi-level index exists
for date, row in ticker_data.iterrows():
rows.append({
"ticker": ticker,
"date": date.strftime("%Y-%m-%d"),
"open": round(row["Open"], 2),
"high": round(row["High"], 2),
"mid": round((row["High"] + row["Low"]) / 2, 2),
"low": round(row["Low"], 2),
"close": round(row["Close"], 2),
"volume": int(row["Volume"]),
})
self.dict_data = sorted(rows, key=lambda x: (x["date"], x["ticker"]), reverse=True)
First, we declare the State variables, which are any fields in your app that may change over time (A Var is directly rendered into the front end of the app):
- The
datastate variable stores the raw stock data fetched from Yahoo Finance. We transform this data to round the values and store it as a list of dictionaries, which is the format that AG Grid expects. - The transformed data is sorted by date and ticker in descending order and stored in the
dict_datastate variable. - The
datetime_nowstate variable stores the current datetime when the data was fetched.
The fetch_stock_data function fetches stock data for the specified companies and transforms it into a format suitable for display in AG Grid. We call this function when clicking on a button, by linking the on_click trigger of the button to this state function:
rx.button(
"Fetch Latest Data",
on_click=State.fetch_stock_data,
)
Defining the AG Grid columns
The column_defs list defines the columns to be displayed in the AG Grid:
column_defs = [
ag_grid.column_def(field="ticker", filter=ag_grid.filters.text, checkbox_selection=True),
ag_grid.column_def(field="date", filter=ag_grid.filters.date),
ag_grid.column_def(field="open", filter=ag_grid.filters.number),
ag_grid.column_def(field="high", filter=ag_grid.filters.number),
ag_grid.column_def(field="low", filter=ag_grid.filters.number),
ag_grid.column_def(field="close", filter=ag_grid.filters.number),
ag_grid.column_def(field="volume", filter=ag_grid.filters.number),
]
fieldkey represents the id of each column.filterkey is used to insert the filter feature, located below the header of each column.
Displaying AG Grid
Now for the most important part of our app, AG Grid itself:
ag_grid(
id="myAgGrid",
column_defs=column_defs,
row_data=State.dict_data,
pagination=True,
pagination_page_size=20,
pagination_page_size_selector=[10, 20, 50, 100],
theme=State.grid_theme,
on_selection_changed=State.handle_selection,
width="100%",
height="60vh",
)
idis required because it uniquely identifies the Ag-Grid instance on the page.column_defsis the list of column definitions we defined earlier.row_datais the data to be displayed in the grid, which is stored in thedict_dataState var.pagination,pagination_page_sizeandpagination_page_size_selectorparameters enable pagination with specific variables in the grid.themeenables you to set the theme of the grid.
We set theme using the grid_theme State var in the rx.select component. Every state var has a built-in function to set its value for convenience, called set_VARNAME, in this case set_grid_theme:
class State(rx.State):
...
# The theme of the AG Grid
grid_theme: str = "quartz"
# The list of themes for the AG Grid
themes: list[str] = ["quartz", "balham", "alpine", "material"]
rx.select(
State.themes,
value=State.grid_theme,
on_change=State.set_grid_theme,
size="1",
)
The on_selection_changed event trigger, shown in the code above, is called when the user selects a row in the grid. This calls the function handle_selection method in the State class, which sets the selected_rows state var to the newly selected row and calls the function update_line_graph.
The update_line_graph function gets the relevant ticker and uses it to set the company state var. The Date, Mid, and DateDifference data for that company for the past 6 months is then set to the state var dff_ticker_hist.
Finally, it is rendered in a line chart, using an error bar to show the DateDifference data which are the highs and the lows for the day.
class State(rx.State):
...
# The selected rows in the AG Grid
selected_rows: list[dict] = None
# The currently selected company in AG Grid
company: str
# The data fetched from Yahoo Finance
data: pd.DataFrame
# The data to be displayed in the line graph
dff_ticker_hist: list[dict] = None
def handle_selection(self, selected_rows, _, __):
self.selected_rows = selected_rows
self.update_line_graph()
def update_line_graph(self):
if self.selected_rows:
ticker = self.selected_rows[0]["ticker"]
else:
self.dff_ticker_hist = None
return
self.company = ticker
dff_ticker_hist = self.data[ticker].reset_index()
dff_ticker_hist["Date"] = pd.to_datetime(dff_ticker_hist["Date"]).dt.strftime("%Y-%m-%d")
dff_ticker_hist["Mid"] = (dff_ticker_hist["Open"] + dff_ticker_hist["Close"]) / 2
dff_ticker_hist["DayDifference"] = dff_ticker_hist.apply(
lambda row: [row["High"] - row["Mid"], row["Mid"] - row["Low"]], axis=1
)
self.dff_ticker_hist = dff_ticker_hist.to_dict(orient="records")
rx.recharts.line_chart(
rx.recharts.line(
rx.recharts.error_bar(
data_key="DayDifference",
direction="y",
width=4,
stroke_width=2,
stroke="red",
),
data_key="Mid",
),
rx.recharts.x_axis(data_key="Date"),
rx.recharts.y_axis(domain=["auto", "auto"]),
data=State.dff_ticker_hist,
width="100%",
height=300,
)
Conclusion
By integrating AG Grid into the Reflex ecosystem, we're empowering Python developers to easily create sophisticated, data-rich web applications. Whether you're building complex dashboards, data analysis tools, or an application that demands powerful data grid capabilities, Reflex AG Grid has you covered.
We're excited to see what you'll build with Reflex AG Grid! Share your projects, ask questions, and join the discussion in the Reflex community forums.
Other Tools and Extensions
For more information on other AG Grid integrations, visit our community tools and extensions page where we showcase community-built integrations for languages like SolidJS, Laravel, Rust and more.
